How do dermatologists get rid of acne?
Uncover 'How do dermatologists get rid of acne?' Explore professional insights into effective acne treatment strategies and clear skin solutions.
How do dermatologists get rid of acne?
Dermatologists employ a range of effective acne treatment methods to help patients achieve clear skin. Treatment options vary depending on factors such as the type and severity of the acne, previous treatments, age, and scarring. By assessing these factors, dermatologists can prescribe the most suitable treatment for individual cases.
Key Takeaways:
- Dermatologists assess the type and severity of acne before determining the appropriate treatment.
- Common treatment options include topical medications like retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid.
- Oral medications like antibiotics and isotretinoin may be prescribed for more severe cases of acne.
- Procedures and therapies such as corticosteroid injections, light therapy, chemical peels, and drainage and extraction of comedos or cysts can be effective in managing acne.
- Practicing a good skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing, is important to prevent future breakouts.
Types of Acne and Assessment by Dermatologists
Before initiating treatment, dermatologists carefully evaluate the type and severity of acne to provide individualized treatment recommendations. Acne comes in various forms, including:
- Whiteheads and blackheads (comedones): These occur when pores become clogged with excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
- Papules: These are small red bumps that can be tender to the touch.
- Pustules: Pustules are inflamed lesions filled with pus, usually appearing as a red circle with a white or yellow center.
- Nodules: Nodules are large, solid, painful bumps that form deep beneath the skin's surface.
- Cysts: Cysts are similar to nodules but are filled with pus and can cause scarring.
Assessing the type and severity of acne helps dermatologists determine the most suitable treatment options. Mild acne, characterized by blackheads and whiteheads, usually responds well to topical medications like retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid. Moderate acne, which includes papules and pustules, often requires a combination of topical treatments and oral medications such as antibiotics. Severe acne, with nodules and cysts, may necessitate a more aggressive approach, including oral isotretinoin and procedures like corticosteroid injections or drainage and extraction of comedos or cysts.
During the assessment process, dermatologists also take into account factors such as the location of acne, previous treatments that may have been ineffective, the patient's age, and the presence of scarring. This personalized approach allows dermatologists to tailor treatment plans that address the unique needs of each individual.
Topical medications for acne treatment
Dermatologists often prescribe topical medications such as retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid to effectively manage acne. These medications are applied directly to the skin and work by targeting the main factors that contribute to acne development, including excess oil production, clogged pores, and inflammation. Here's a closer look at these commonly recommended topical treatments:
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids help unclog pores and reduce inflammation. They also promote cell turnover, preventing the formation of new acne lesions. Commonly prescribed retinoids include tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene.
- Benzoyl peroxide: This ingredient kills acne-causing bacteria and helps remove excess oil and dead skin cells. It is available over-the-counter in various strengths and is often combined with other topical medications for enhanced efficacy.
- Azelaic acid: Azelaic acid has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it effective in treating mild to moderate acne. It also helps unclog pores and reduces the production of abnormal skin cells.
In addition to these key medications, dermatologists may also recommend other topical treatments based on individual needs. These can include antibiotics in the form of topical creams or gels to kill bacteria, as well as topical dapsone to reduce inflammation.
Combining treatments for optimal results
Every case of acne is unique, so dermatologists may prescribe a combination of topical medications to achieve the best results. For example, retinoids are often used in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide or azelaic acid to address multiple acne-causing factors simultaneously. Dermatologists will consider the type and severity of acne, as well as any potential side effects, when determining the most suitable combination of treatments for each individual.
It is important to note that topical medications may cause side effects such as dryness, redness, or peeling of the skin. These effects are typically mild and can be managed with proper skincare routines and adjusting the frequency or strength of medication use. It is always recommended to consult with a dermatologist who can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the acne treatment process.
Section 4: Oral Medications and Other Systemic Treatments
In cases of severe acne, dermatologists may prescribe oral medications such as antibiotics or isotretinoin to help control the condition. These medications are often used when topical treatments alone are not sufficient to manage the acne effectively. Here are some common types of oral medications dermatologists may recommend:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics like tetracycline, erythromycin, or doxycycline can help reduce acne-causing bacteria and inflammation within the skin.
- Isotretinoin: This powerful medication is reserved for severe cases of acne that do not respond to other treatments. Isotretinoin works by reducing oil production and preventing clogged pores.
It is important to note that these oral medications may have potential side effects and must be taken under the supervision of a dermatologist. Routine check-ups and monitoring are typically required throughout the duration of the treatment to ensure its safety and efficacy.
Alongside oral medications, dermatologists may also recommend other systemic treatments for severe acne. These treatments can include:
- Corticosteroid Injections: For severe and painful acne breakouts, dermatologists may administer corticosteroid injections directly into the inflamed lesions to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Light Therapy: Some dermatologists utilize light therapy, such as blue light or photodynamic therapy, to target and kill acne-causing bacteria.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels can help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores, leading to a reduction in acne. They work by applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes controlled exfoliation.
- Drainage and Extraction: When dealing with stubborn comedos or cysts, dermatologists may perform drainage and extraction procedures to remove the contents and alleviate inflammation.
- Steroid Injections: Nodular or cystic acne lesions can be treated with steroid injections to reduce swelling and pain.
It is crucial to consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific case of acne. They will consider various factors, such as the type and severity of acne, previous treatments, medical history, and individual needs, to create an effective and personalized approach.
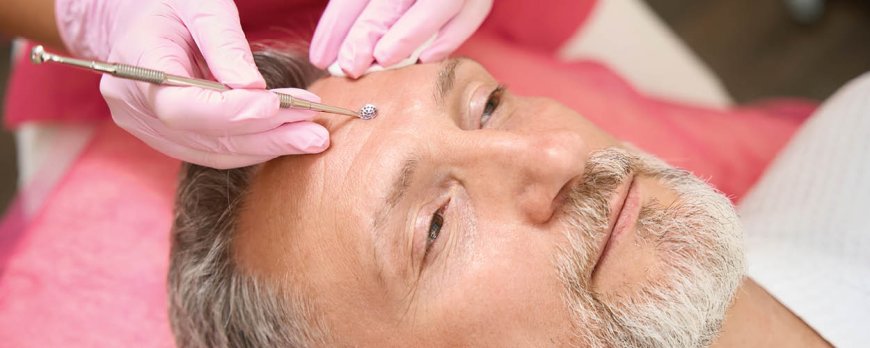
Procedures and Therapies for Acne Management
Dermatologists employ a range of procedures and therapies, such as corticosteroid injections, light therapy, chemical peels, and drainage and extraction of comedos or cysts, to manage acne and promote clear skin. These treatment options target different aspects of acne, providing effective solutions for both moderate and severe cases.
Corticosteroid Injections
For those frustrating, deep, and painful nodular or cystic lesions, corticosteroid injections can be a game-changer. Dermatologists use a fine needle to inject a diluted corticosteroid into the lesion, reducing inflammation and promoting rapid healing. This procedure provides quick relief and helps prevent scarring, making it an excellent option for severe breakouts.
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, utilizes specific wavelengths of light to target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. Dermatologists may recommend different types of light therapy, including blue light and red light therapies. Blue light targets the bacteria responsible for acne, while red light helps calm inflammation and promote healing. This non-invasive procedure is generally well-tolerated and can be used in combination with other treatments.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are another popular option for managing acne. During this procedure, a solution containing various chemicals, such as salicylic acid or glycolic acid, is applied to the skin. The solution exfoliates the top layer of the skin, unclogs pores, and promotes the growth of new, healthier skin. Chemical peels can improve acne scarring, reduce the appearance of blemishes, and enhance overall skin texture.
Drainage and Extraction
When comedos or cysts become especially stubborn or painful, dermatologists may perform drainage and extraction to release the trapped contents. This procedure involves carefully opening the affected area and removing the accumulated oil, bacteria, and debris. By relieving pressure and eliminating blockages, drainage and extraction can speed up the healing process and prevent further breakouts.
When it comes to managing acne, dermatologists have an arsenal of procedures and therapies at their disposal. From corticosteroid injections to light therapy, chemical peels to drainage and extraction, these interventions are tailored to address different types and severities of acne. By working with a dermatologist, individuals can benefit from personalized treatment plans that target their specific acne concerns and help them achieve clear, healthy skin.
Importance of good skincare routines
Dermatologists emphasize the importance of establishing a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing to maintain clear and healthy skin. By incorporating these practices into your daily skincare regimen, you can effectively manage acne and promote overall skin health.
Gentle cleansing is vital in removing dirt, excess oil, and impurities from the skin. Opt for a mild cleanser that is specifically formulated for acne-prone skin, as harsh or abrasive cleansers can strip the skin of its natural oils and further aggravate acne. Gently massage the cleanser onto your face using circular motions, and rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water.
Exfoliating helps to unclog pores and remove dead skin cells that can contribute to acne breakouts. Choose a gentle exfoliating scrub or a chemical exfoliant containing ingredients like salicylic acid or glycolic acid. Incorporate exfoliation into your skincare routine once or twice a week to maintain a smooth and clear complexion.
Moisturizing is crucial for maintaining the skin's hydration levels and preventing excessive dryness. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers that won't clog your pores. Applying a lightweight moisturizer after cleansing and exfoliating helps to balance the skin's moisture levels and keep it hydrated without causing breakouts.
Lifestyle changes for acne management
Dermatologists advise making certain lifestyle changes to help manage acne. By adopting these habits, individuals can improve their skin health and reduce the frequency and severity of breakouts. Here are some recommended lifestyle changes:
- Avoid pore-clogging skincare products: Opt for non-comedogenic or oil-free skincare products that won't clog pores. Look for labels that specifically mention being suitable for acne-prone skin.
- Protect the skin from harmful UV rays: Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, even on cloudy days. This helps protect the skin from sun damage and prevents the darkening of acne scars.
- Keep the hands away from the face: Touching the face can transfer bacteria and oil to the skin, exacerbating acne. Avoid picking or popping pimples, as this can lead to inflammation and scarring.
- Wash your face twice a day: Use a gentle cleanser to wash the face in the morning and at night. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as it can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Avoid excessive exfoliation: While exfoliating can help unclog pores, overdoing it can strip the skin of its natural oils and cause irritation. Stick to exfoliating once or twice a week to avoid aggravating acne.
Remember, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to manage severe acne. It is essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan tailored to individual needs. Dermatologists can provide personalized recommendations and prescribe appropriate medications or therapies to effectively treat acne.
Alternative and integrative medicine approaches
Some individuals may find alternative and integrative medicine approaches, such as using tea tree oil or brewer's yeast, helpful in managing acne, as recommended by dermatologists. These natural remedies have gained popularity due to their potential antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil is extracted from the leaves of the tea tree plant. It has been used traditionally for its antimicrobial effects and is believed to help reduce acne lesions. Tea tree oil can be applied topically to acne-prone areas, but it is important to dilute it properly before use to prevent skin irritation.
Brewer's yeast: Brewer's yeast, also known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a type of fungus commonly used in brewing beer and baking. It contains various vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that may promote healthy skin. Some studies suggest that brewer's yeast may help reduce acne by inhibiting the growth of acne-causing bacteria and reducing inflammation. It can be taken as a supplement or applied topically in the form of masks or creams.
While alternative and integrative medicine approaches can be beneficial for some individuals, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist before incorporating them into your acne management routine. Dermatologists can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific skin type, medical history, and acne severity. They can also help you understand the potential risks and benefits associated with these alternative treatments.

Conclusion
Dermatologists offer a wide range of effective treatments and elimination methods to help individuals effectively manage and eliminate acne. By assessing the type and severity of the acne, dermatologists can prescribe appropriate treatment options tailored to each individual's needs. Factors such as the type and location of the acne, previous treatments, age, and scarring are taken into consideration when determining the best course of action.
Topical medications, such as retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid, are commonly recommended by dermatologists for treating acne. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of acne and reducing inflammation and bacterial growth. In some cases, oral medications like antibiotics and isotretinoin may be prescribed for more severe forms of acne.
Dermatologists also utilize various procedures and therapies to manage acne effectively. Corticosteroid injections are used to reduce inflammation and quickly resolve severe breakouts. Light therapy and chemical peels can help improve acne by reducing oil production and promoting skin cell turnover. Additionally, drainage and extraction of comedos or cysts are performed to alleviate discomfort and prevent the formation of new breakouts.
While treating acne, dermatologists stress the importance of adopting good skincare routines. Gentle cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing are key steps to maintain healthy skin and prevent future breakouts. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding pore-clogging skincare products and protecting the skin from the sun, are also recommended to manage acne effectively.
For those seeking alternative approaches, dermatologists may suggest using ingredients like tea tree oil and brewer's yeast, which have been found to have acne-fighting properties. However, it is important to consult with a dermatologist before incorporating these alternative methods into a treatment plan.
In conclusion, dermatologists offer a comprehensive approach to acne treatment, considering the unique needs of each individual. With their expertise, they can provide effective treatments and elimination methods, helping individuals achieve clearer and healthier skin. It is always recommended to consult a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for individual cases of acne.
FAQ
How do dermatologists get rid of acne?
Dermatologists treat acne by assessing the type and severity of the acne, and then prescribing appropriate treatment options. Treatments can vary depending on factors such as the type of acne, where it appears on the skin, previous treatments, age, and scarring.
What are some common treatment options recommended by dermatologists?
Some common treatment options for acne include topical medications like retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid; oral medications like antibiotics and isotretinoin; corticosteroid injections for severe breakouts; light therapy; chemical peels; drainage and extraction of comedos or cysts; and steroid injections for nodular or cystic lesions.
How important is a good skincare routine in managing acne?
Dermatologists emphasize the significance of adopting a good skincare routine, including gentle cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing, to prevent future breakouts.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage acne?
Dermatologists recommend making lifestyle changes such as avoiding certain skincare products and protecting the skin from the sun to effectively manage acne.
Are there any alternative or integrative medicine approaches for acne?
Some alternative and integrative medicine approaches, such as tea tree oil and brewer's yeast, may be effective for acne management. However, it is important to consult a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for individual cases of acne.



































































































































