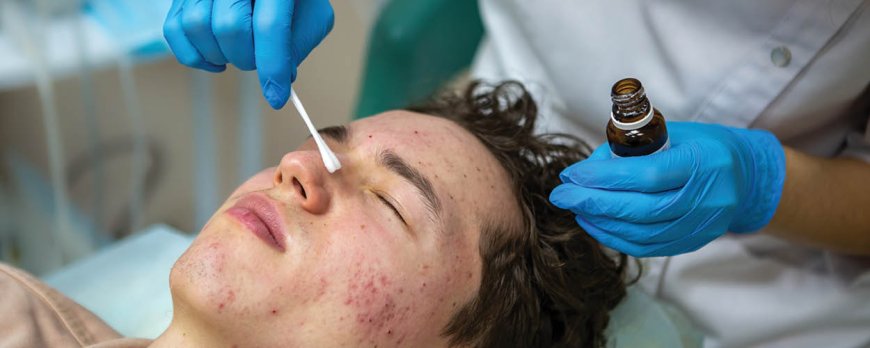
Is cystic acne hormonal or bacterial?
Explore the causes behind cystic acne: Is cystic acne hormonal or bacterial? Uncover the facts and debunk the myths surrounding this skin condition.

Is cystic acne hormonal or bacterial?
Cystic acne is a severe form of acne that can be influenced by both hormonal imbalances and bacterial factors. Hormonal acne is triggered by hormonal fluctuations and is common during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. It appears as deep, red, and tender cysts mostly on the lower parts of the face, such as the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks. Bacterial acne, on the other hand, is caused by bacterial overgrowth, inflammation, and increased sebum production. It is characterized by inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts that are frequently red and tender to the touch and is often found on oily skin areas like the forehead, nose, and chin. Determining whether acne is hormonal or bacterial can be done by considering patterns such as hormonal fluctuations and by consulting a dermatologist. Treatment options include topical medications, oral medications, lifestyle changes, and consistent skincare routines tailored to the specific type of acne.
Key Takeaways:
- Cystic acne can be influenced by both hormonal imbalances and bacterial factors.
- Hormonal acne is triggered by hormonal fluctuations and is common during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
- Bacterial acne is caused by bacterial overgrowth, inflammation, and increased sebum production.
- Observing patterns and consulting a dermatologist can help determine whether acne is hormonal or bacterial.
- Treatment options for cystic acne include topical and oral medications, lifestyle changes, and consistent skincare routines.
Understanding Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne is commonly triggered by fluctuations in hormone levels and can occur during various life stages, such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. These hormonal imbalances can lead to an increased production of sebum, or oil, in the skin, which can clog pores and result in acne breakouts.
One of the key characteristics of hormonal acne is the presence of deep, red, and tender cysts that often appear on the lower parts of the face, such as the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks. These cysts can be painful and take longer to heal compared to other types of acne. Hormonal acne can also manifest as blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed pimples.
When it comes to treating hormonal acne, there are various options available. Topical medications that contain ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help to unclog pores and reduce inflammation. Oral medications, such as hormonal birth control or spironolactone, may also be prescribed by a dermatologist to regulate hormone levels and manage acne. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress levels, and practicing good skincare habits can all contribute to the effective treatment of hormonal acne.
If you are experiencing persistent or severe hormonal acne, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. They can provide personalized recommendations and treatment plans based on your specific needs. With the right approach, hormonal acne can be effectively managed, leading to clearer and healthier skin.
Exploring Bacterial Acne
Bacterial acne is primarily caused by the overgrowth of bacteria, inflammation, and excessive sebum production, leading to the formation of acne lesions. When certain strains of bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, accumulate on the skin, they can clog pores and trigger an immune response, resulting in the development of acne. The bacteria feed on the sebum produced by the skin, creating an ideal environment for further proliferation and inflammation.
Bacterial acne typically presents as inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts that are often red and tender to the touch. These lesions tend to occur on areas of the skin that are more prone to oiliness, such as the forehead, nose, and chin. They can be painful and may, in severe cases, leave behind marks or scars. The severity of bacterial acne can vary from mild to severe, requiring different treatment approaches.
To effectively treat bacterial acne, it is important to address both the bacteria and the underlying causes of inflammation and excessive sebum production. Topical medications containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can help kill bacteria, reduce inflammation, and unclog pores. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to target the bacterial overgrowth and reduce inflammation systemically.
In addition to medications, incorporating good skincare practices into one's routine is essential for managing bacterial acne. Regular cleansing, using non-comedogenic products, and avoiding harsh or irritating substances can help maintain a healthy skin barrier and prevent further acne breakouts. It is also important to resist the urge to pick or pop acne lesions, as this can lead to further inflammation and potential scarring.
Differentiating Hormonal and Bacterial Acne
Differentiating between hormonal and bacterial acne can be done by examining the specific characteristics of the acne lesions and considering patterns such as hormonal fluctuations. Hormonal acne typically presents as deep, red, and tender cysts predominantly on the lower parts of the face, including the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks. These cysts can be persistent and take longer to heal compared to other types of acne. On the other hand, bacterial acne is characterized by inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts that are frequently red and tender to the touch. It is commonly found on oily skin areas like the forehead, nose, and chin.
To determine the underlying cause of acne, it is essential to observe any patterns or changes in outbreaks. Hormonal acne is often associated with hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. If the acne outbreaks coincide with these hormonal changes, it is more likely to be hormonal acne. However, consulting a dermatologist is the best course of action to receive a professional diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Signs of Hormonal Acne:
- Deep, red, and tender cysts
- Occurs predominantly on lower face (jawline, chin, neck, cheeks)
- Associated with hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause
Signs of Bacterial Acne:
- Inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts
- Red and tender to the touch
- Commonly found on oily skin areas like forehead, nose, and chin
Once the underlying cause of acne has been determined, appropriate treatment options can be explored. Hormonal acne can be managed with topical medications, oral medications, and lifestyle changes that address hormonal imbalances. Bacterial acne, on the other hand, often requires the use of topical medications, oral antibiotics, and other therapies to address bacterial overgrowth and inflammation. It is important to establish a consistent skincare routine tailored to the specific type of acne for effective management.

Determining the cause of acne
Determining the cause of acne, whether hormonal or bacterial, requires careful observation of patterns and consultation with a dermatologist. By paying attention to the timing and location of acne outbreaks, you can gain valuable insights into the underlying cause. Hormonal acne is often characterized by breakouts that coincide with hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. These blemishes typically appear as deep, red, and tender cysts primarily on the lower parts of the face, such as the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks.
On the other hand, bacterial acne is caused by an overgrowth of bacteria, inflammation, and increased sebum production. It is commonly found in areas with oily skin like the forehead, nose, and chin. Bacterial acne manifests as inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts that are frequently red and tender to the touch.
If you are unsure whether your acne is hormonal or bacterial, it is always best to seek professional advice from a dermatologist. They can closely examine your skin, consider your medical history, and provide an accurate diagnosis. A dermatologist may conduct hormone tests or take bacterial cultures to determine the root cause of your acne. This personalized approach ensures that you receive the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition.
When it comes to treating hormonal or bacterial acne, there are various options available. Topical medications, such as retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or antibiotics, can be effective in reducing inflammation and clearing up blemishes. In some cases, oral medications like oral contraceptives or antibiotics may be prescribed to regulate hormones or target bacteria internally. Additionally, making certain lifestyle changes, including maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good hygiene, and managing stress levels, can support acne management. Tailoring your skincare routine to address either hormonal or bacterial acne can also significantly improve the condition of your skin.
Treating hormonal acne
Treating hormonal acne involves a combination of topical and oral medications, as well as lifestyle adjustments to address hormonal imbalances. Here are some key treatment approaches:
- Topical medications: Topical creams or gels containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help reduce inflammation, unclog pores, and prevent future breakouts. These medications are typically applied directly to the affected areas of the skin.
- Oral medications: In more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe oral medications such as antibiotics or hormonal contraceptives to help regulate hormones and control acne outbreaks. These medications work from within to address the underlying hormonal imbalances contributing to acne.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also play a crucial role in managing hormonal acne. Maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding triggers like greasy or sugary foods, and staying well-hydrated can all help support overall skin health. Additionally, managing stress levels through activities like exercise, meditation, or counseling can also help regulate hormones and reduce acne severity.
It's important to note that treating hormonal acne may require patience and consistency. Results may not be immediate, and it may take several weeks or months to see improvement. Consulting with a dermatologist is recommended to determine the best treatment plan for individual needs.
Treating Bacterial Acne
The treatment of bacterial acne typically involves a combination of topical medications, oral antibiotics, and other therapies to address bacterial overgrowth and reduce inflammation. These treatment options aim to target the underlying causes of bacterial acne and promote clearer, healthier skin.
Topical medications: Dermatologists often prescribe topical medications containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids to help eliminate bacteria, reduce inflammation, and unclog pores. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas and can be effective in treating bacterial acne.
Oral antibiotics: In some cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral antibiotics to help fight the bacterial overgrowth contributing to acne. Antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline work by reducing inflammation and targeting the bacteria that cause acne. Oral antibiotics are typically used for a short period to avoid antibiotic resistance.
Other therapies: In addition to topical medications and oral antibiotics, there are other therapeutic options available for treating bacterial acne. These may include procedures like acne extractions, chemical peels, or laser treatments, which can help to effectively clear acne and improve the appearance of the skin.
Preventing Bacterial Acne
While treatment is essential for managing bacterial acne, prevention is also crucial. Here are some tips to help prevent bacterial acne outbreaks:
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine, using gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic products to keep the skin clean and free from excess oil.
- Avoid touching the face, as this can transfer bacteria and irritate the skin, leading to acne breakouts.
- Wash pillowcases and other bedding regularly to prevent the accumulation of bacteria and oil that can contribute to acne.
- Minimize stress levels, as stress can trigger hormonal changes that may worsen acne. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limiting the consumption of sugary and greasy foods can help reduce inflammation and improve overall skin health.
By combining appropriate treatment methods with preventive measures, it is possible to manage bacterial acne effectively and minimize its impact on daily life.

Lifestyle changes for acne management
Making certain lifestyle changes, such as following a balanced diet, practicing good hygiene, and managing stress, can complement acne treatment and help manage both hormonal and bacterial acne. By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can support the effectiveness of your chosen acne treatments and promote clearer, healthier skin.
1. Follow a balanced diet:
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide your body with essential nutrients that promote skin health. Avoiding sugary, processed foods and limiting dairy consumption may also help reduce acne breakouts.
2. Practice good hygiene:
Keeping your skin clean is crucial for managing acne. Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and bacteria. Avoid harsh scrubbing and opt for non-comedogenic skincare products to prevent clogged pores.
3. Manage stress:
Stress can increase inflammation in the body, leading to acne flare-ups. Find stress management techniques that work for you, such as regular exercise, deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in hobbies. Prioritizing self-care and relaxation can contribute to healthier skin.
Remember, acne treatment is not one-size-fits-all. While these lifestyle changes can support acne management, it is essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the underlying cause of your acne and develop a personalized treatment plan. With the right combination of lifestyle changes and targeted therapies, you can take control of your acne and achieve clearer, more radiant skin.
Tailoring skincare routines
Establishing a consistent skincare routine tailored to the specific type of acne, whether hormonal or bacterial, is essential for effective acne management. By incorporating the following practices into your daily regimen, you can help reduce acne outbreaks and promote healthier skin:
1. Cleansing:
- Use a gentle cleanser twice a day to remove dirt, excess oil, and bacteria from the skin.
- Avoid harsh scrubs or cleansers that can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Look for cleansers specifically designed for acne-prone skin, containing ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide, which can help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
2. Moisturizing:
- Moisturize daily to keep your skin hydrated and prevent excessive dryness, which can lead to increased oil production and breakouts.
- Choose oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers that won't clog pores or contribute to acne formation.
- Look for moisturizers that contain ingredients like hyaluronic acid or ceramides, which help maintain the skin's moisture barrier.
3. Targeted treatments:
- Consider incorporating topical treatments into your routine to directly address acne symptoms.
- For hormonal acne, look for products containing ingredients like retinoids or hormonal agents, such as spironolactone, under the guidance of a dermatologist.
- For bacterial acne, products with ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or topical antibiotics can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Remember to be consistent with your skincare routine, as results may take time to appear. Additionally, avoid picking or popping acne lesions, as this can lead to scarring and further infection. If you're uncertain about which products or treatments are best for your specific acne condition, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and recommendations.
Seeking Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice from a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and effective treatment plans for managing hormonal or bacterial acne. Dermatologists are specialized in identifying the underlying causes of acne and can recommend suitable treatments based on individual skin types and concerns. By consulting a professional, you can gain valuable insights into your specific acne triggers and receive targeted recommendations for achieving clearer skin.
Dermatologists can conduct thorough evaluations and assessments to determine whether your acne is primarily hormonal or bacterial. They will take into account your medical history, lifestyle factors, and any patterns or changes in your acne outbreaks. This comprehensive approach helps in tailoring treatment plans that address the root cause of your acne, ensuring long-term management and prevention of future breakouts.
During the consultation, dermatologists may recommend a combination of treatment options depending on the type and severity of your acne. These can include topical medications, such as retinoids or antibiotics, to target inflammation and bacterial overgrowth. Oral medications, such as hormonal birth control or isotretinoin, may be prescribed for hormonal acne that is resistant to topical treatments. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, like dietary changes and stress management techniques, can be advised to support overall skin health.
In addition to providing medical treatment, dermatologists can also provide guidance on establishing a consistent skincare routine tailored to your specific acne type. They can recommend suitable cleansers, moisturizers, and targeted treatments that can help address your acne concerns. Regular follow-up appointments with a dermatologist can ensure that your treatment plan is effective and make any necessary adjustments to optimize your results.
Conclusion
Cystic acne can be influenced by both hormonal imbalances and bacterial factors, highlighting the need to address both causes for effective treatment and management. Hormonal acne, triggered by fluctuations in hormones, is commonly experienced during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. It manifests as deep, red, and tender cysts predominantly on the lower parts of the face, such as the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks. Conversely, bacterial acne is caused by an overgrowth of bacteria, inflammation, and increased sebum production. It is characterized by inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts, often appearing red and tender to the touch, particularly on oily skin areas like the forehead, nose, and chin.
Determining whether acne is hormonal or bacterial can be achieved by observing patterns, considering hormonal fluctuations, and consulting with a dermatologist. By understanding the underlying cause, appropriate treatment options can be pursued. Topical medications, oral medications, lifestyle changes, and consistent skincare routines tailored to the specific type of acne are available for management.
Addressing hormonal imbalances in hormonal acne may involve interventions to regulate hormonal fluctuations, such as oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, or certain medications. On the other hand, targeting bacterial causes in bacterial acne may involve the use of topical medications, oral antibiotics, or other therapies to combat bacterial overgrowth and inflammation. Lifestyle changes, including maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good hygiene, managing stress levels, and avoiding potential triggers, can help control acne outbreaks. Additionally, establishing a skincare regimen tailored to the specific type of acne, with suitable cleansers, moisturizers, and targeted treatments, is essential.
To ensure effective treatment and management of cystic acne, it is crucial to seek professional advice from a dermatologist. They can provide personalized guidance, recommend appropriate treatment plans, and monitor progress. By addressing both hormonal imbalances and bacterial factors, individuals can take proactive steps towards clearer and healthier skin.
FAQ
Is cystic acne hormonal or bacterial?
Cystic acne can be caused by hormonal imbalances or bacterial concerns.
What causes hormonal acne?
Hormonal acne is triggered by hormonal fluctuations and is common during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
What are the characteristics of hormonal acne?
Hormonal acne appears as deep, red, and tender cysts mostly on the lower parts of the face, such as the jawline, chin, neck, or cheeks.
What causes bacterial acne?
Bacterial acne is caused by bacterial overgrowth, inflammation, and increased sebum production.
How does bacterial acne appear?
Bacterial acne is characterized by inflamed pimples, pustules, and cysts that are frequently red and tender to the touch and is often found on oily skin areas like the forehead, nose, and chin.
How can I determine whether my acne is hormonal or bacterial?
Determining whether acne is hormonal or bacterial can be done by considering patterns such as hormonal fluctuations and by consulting a dermatologist.
What are the treatment options for hormonal acne?
Treatment options for hormonal acne include topical medications, oral medications, lifestyle changes, and consistent skincare routines tailored to the specific type of acne.
What are the treatment options for bacterial acne?
Treatment options for bacterial acne include topical medications, oral antibiotics, and other therapies to target the bacterial overgrowth and inflammation.
What lifestyle changes can help manage acne?
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good hygiene, managing stress levels, and avoiding potential triggers can help manage both hormonal and bacterial acne.
How can I tailor my skincare routine for acne management?
Tailoring your skincare routine involves using suitable cleansers, moisturizers, and targeted treatments for different types of acne. It is important to select products and establish a skincare regimen tailored to hormonal or bacterial acne.
When should I seek professional advice for acne?
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment plans if acne becomes persistent or severe.